Power Platform TypeScript Development Workflow - Git Integration with Automated JavaScript Compilation
Modern Power Platform development often requires writing JavaScript web resources for form events, custom logic, and API integrations. However, working directly with JavaScript in Dataverse can be challenging. You lose IntelliSense, type safety, and modern development tooling. Today, I’m excited to share my open-source solution that bridges this gap: the Power Platform JavaScript Compiler.
This project demonstrates a complete TypeScript development workflow for Power Platform web resources, leveraging Git integration to create a seamless development experience that combines the power of TypeScript with the native Power Platform git integration.
The Problem with Traditional Web Resource Development
Developing JavaScript web resources in Power Platform:
- Writing JavaScript directly in the Dataverse web interface
- No IntelliSense or type checking
- Limited debugging capabilities
- Manual file management and version control
- Risk of syntax errors and runtime issues
The Solution: TypeScript + Git Integration
My Power Platform JavaScript Compiler provides:
- Type-safe development with full XRM API typings
- Automated compilation from TypeScript to JavaScript
- Smart file mapping between TypeScript sources and web resources
- Git-based deployment using Power Platform’s native integration
How It Works
The workflow leverages Power Platform’s Git integration feature to create a bidirectional sync between your local development environment and Dataverse:
- Export web resources from Power Platform to Git
- Pull the repository locally for development
- Map web resources to TypeScript files
- Develop using TypeScript with full type safety
- Compile automatically to JavaScript web resources
- Commit changes to Git
- Sync back to Power Platform using Git integration
Step-by-Step Walkthrough
Let me walk you through the complete workflow with real examples:
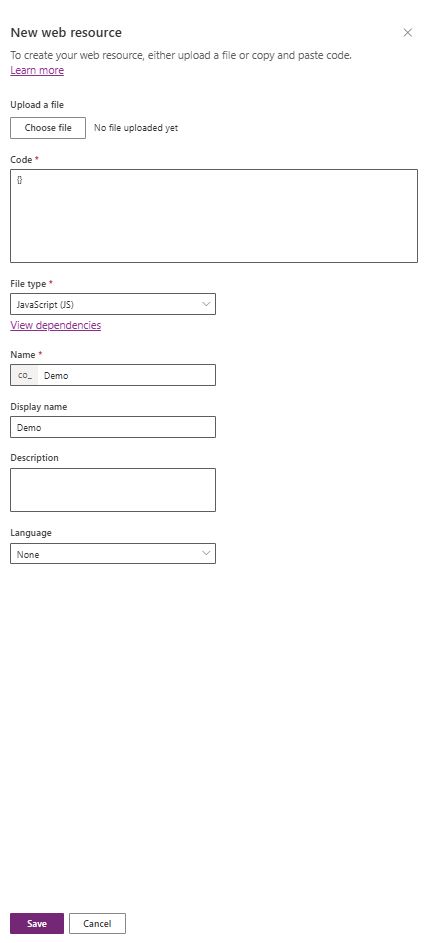
Step 1: Setting Up a New Web Resource
First, create a new web resource in Power Platform. This will be our target for TypeScript development.
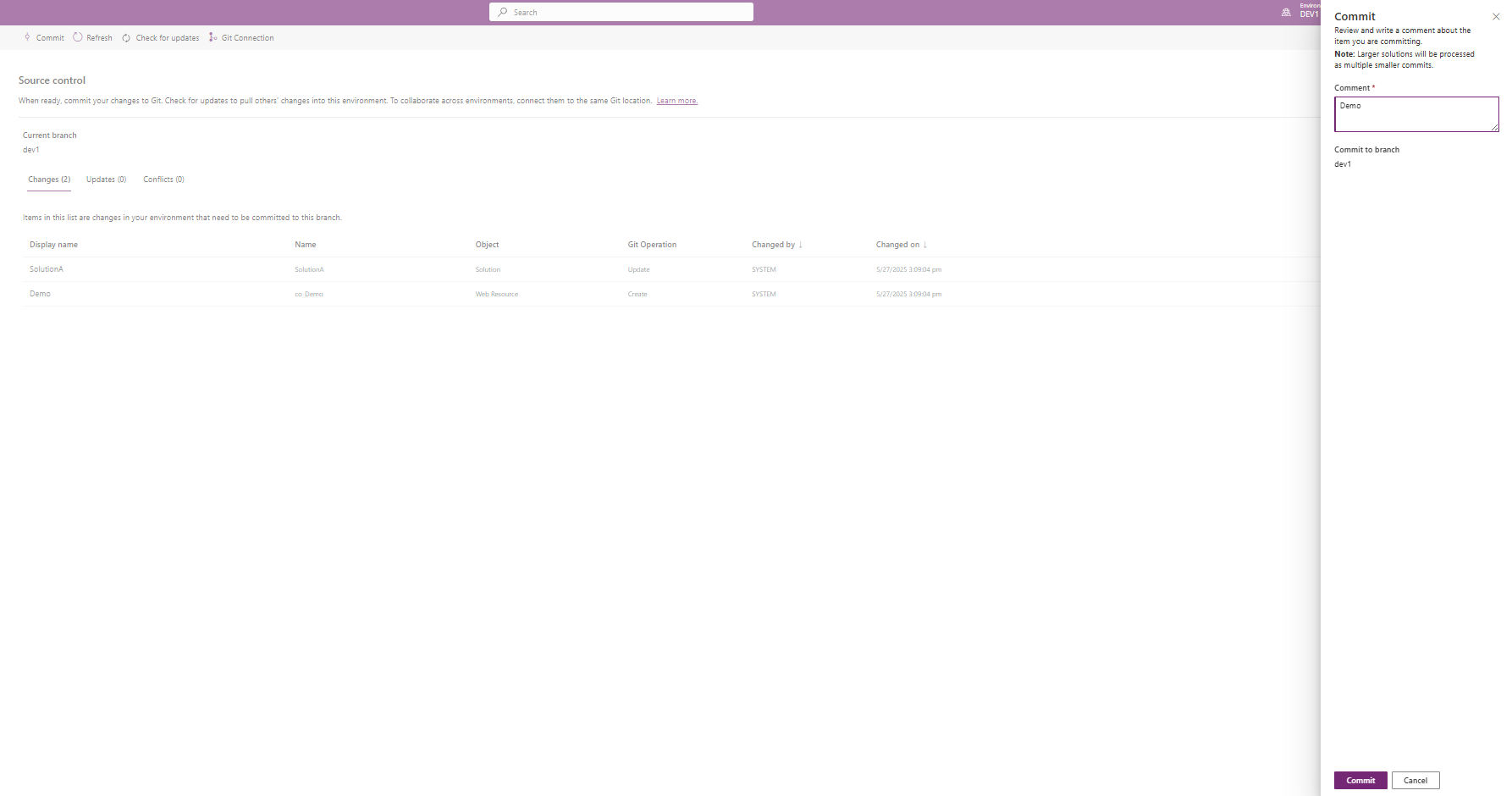
Step 2: Configure Git Integration
Enable Power Platform Git integration to export your solution containing the web resource to source control.
Step 3: Create TypeScript Mapping
After pulling the repository locally, use the provided script to create a mapping between your web resource and a new TypeScript file:
npm run new-webresource
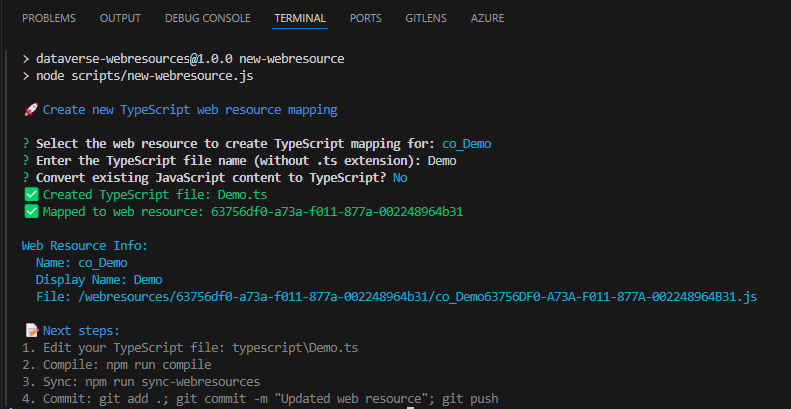
This interactive script will:
- Show all available web resources from your Power Platform export
- Allow you to select which web resource to map
- Create a TypeScript file with proper XRM typings
- Set up the compilation mapping
Step 4: Develop with TypeScript
Now you can write your web resource logic in TypeScript with full IntelliSense and type safety:
namespace MyFormLogic {
export function onLoad(executionContext: Xrm.Events.EventContext): void {
const formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
// Type-safe form operations with IntelliSense
const nameField = formContext.getAttribute("name");
if (nameField) {
nameField.addOnChange(onNameChange);
}
// Type-safe UI operations
formContext.ui.setFormNotification(
"Form loaded successfully",
"INFO",
"load_notification"
);
}
function onNameChange(executionContext: Xrm.Events.EventContext): void {
const attribute = executionContext.getEventSource() as Xrm.Attributes.StringAttribute;
console.log('Name changed to:', attribute.getValue());
}
}
// Make functions available globally for Power Platform
(window as any).MyFormLogic = MyFormLogic;
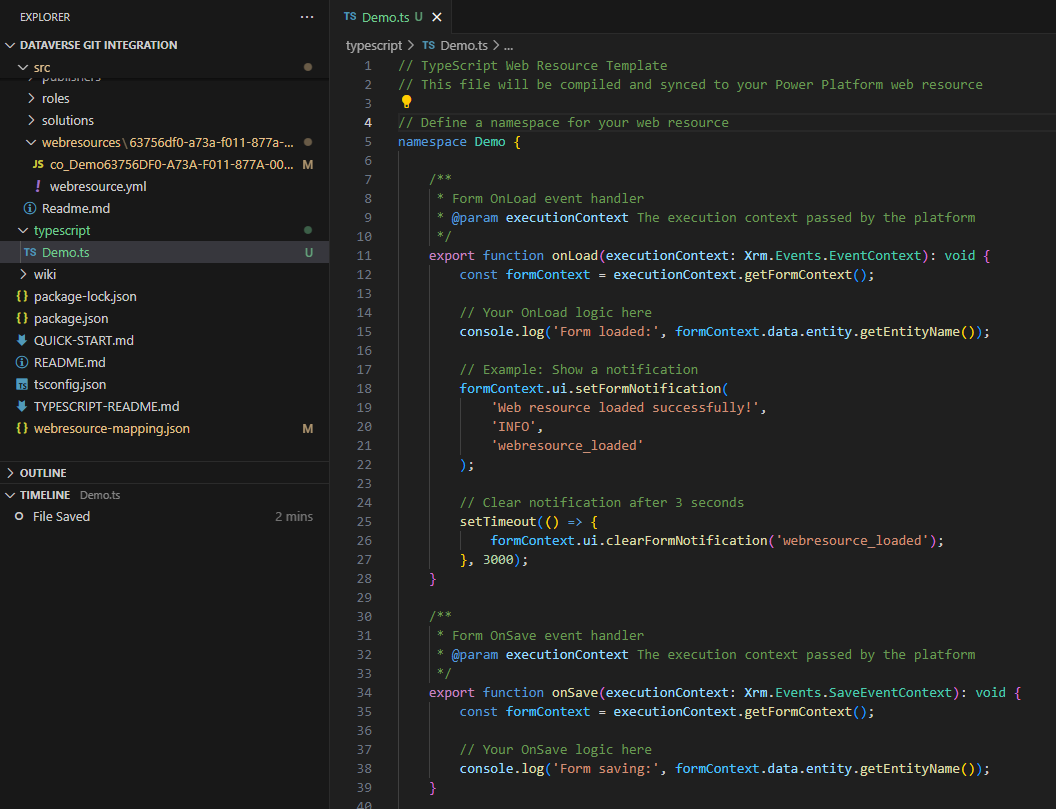
Step 5: Update your logic
Update the typescript with the logic required for your front end.
Step 6: Compile and Sync
Use the development command to compile TypeScript and sync to web resources:
npm run dev
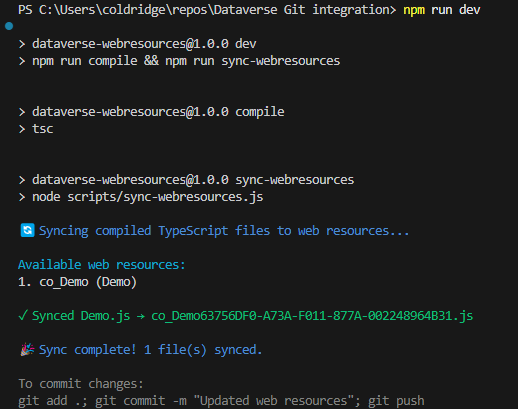
This command:
- Compiles TypeScript to ES2020 JavaScript
- Maps the output to the correct web resource folder
- Preserves the file structure expected by Power Platform
Step 7: Commit to Git
When you’re satisfied with your changes, commit them to Git:
git add .
git commit -m "Enhanced form logic with TypeScript"
git push
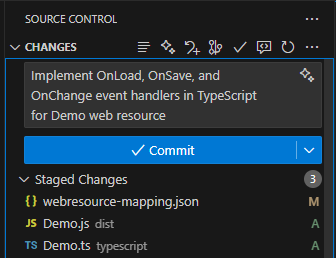
Step 8: Pull into Power Platform
Use Power Platform’s Git integration to pull your changes:
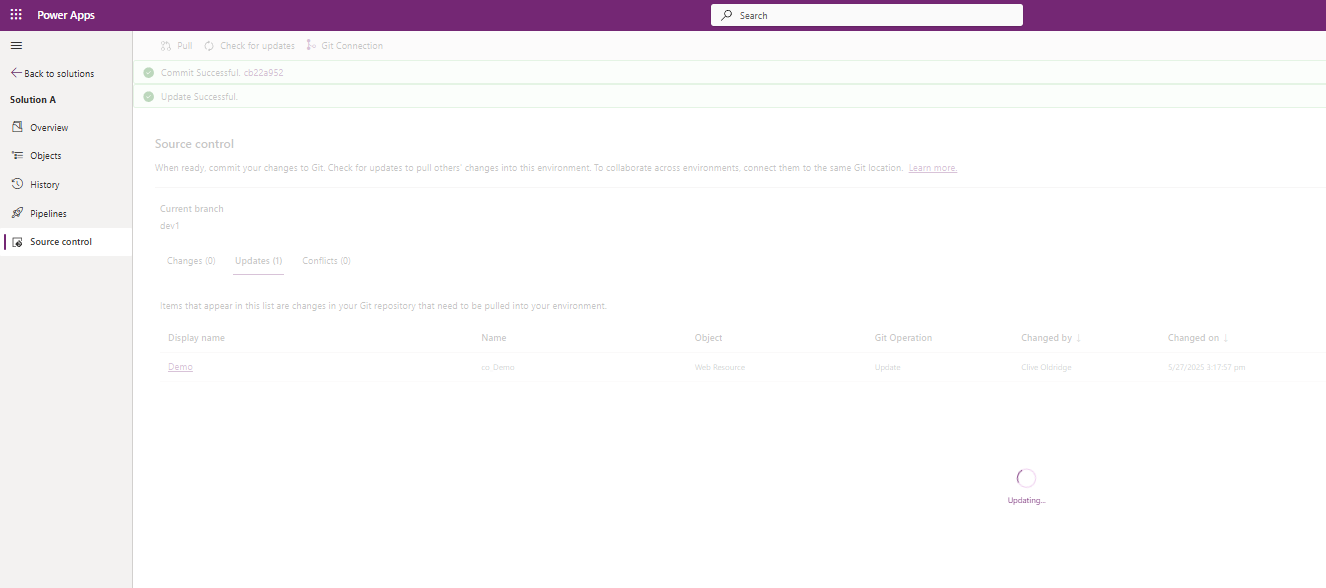
Step 9: Verify in Dataverse
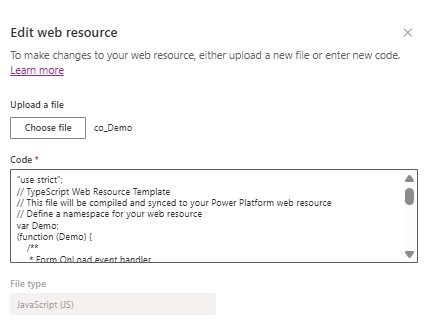
Your compiled JavaScript is now updated in Dataverse, ready for use:
Key Features and Benefits
🚀 Type Safety
- Full XRM API typings included
- Catch errors at compile time, not runtime
- IntelliSense for all Power Platform APIs
🔄 Automated Workflow
- One command compilation and sync
- Smart file mapping system
🛠️ Modern Tooling
- ES2020 target for modern features
- Proper module configuration for Power Platform
- Debug-friendly compiled output
📁 Project Structure
├── typescript/ # Your TypeScript source files
│ ├── form-logic.ts # Form event handlers
│ └── api-integration.ts # API integration logic
├── dist/ # Compiled JavaScript files
├── scripts/ # Build and sync automation
├── src/webresources/ # Power Platform web resources (Git export)
├── package.json # Dependencies and scripts
├── tsconfig.json # TypeScript configuration
└── webresource-mapping.json # File mapping configuration
Available NPM Scripts
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
npm run dev |
Compile and sync (main development command) |
npm run new-webresource |
Create mapping for new web resources |
npm run sync-webresources |
Sync compiled files to web resource folders |
npm run build |
Clean and compile everything |
npm run compile |
Compile TypeScript to JavaScript |
Best Practices
1. Use Namespaces
Wrap your code in namespaces to avoid global conflicts:
namespace AccountFormLogic {
export function onLoad(executionContext: Xrm.Events.EventContext): void {
// Your logic here
}
}
2. Error Handling
Always include proper error handling:
namespace ApiIntegration {
async function callExternalApi(recordId: string): Promise<void> {
try {
const response = await fetch(`/api/data/${recordId}`);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP ${response.status}: ${response.statusText}`);
}
// Process response
} catch (error) {
console.error('API Error:', error);
Xrm.Navigation.openErrorDialog({
message: 'Failed to fetch external data'
});
}
}
}
3. Form Context Validation
Always check form context availability:
export function onFieldChange(executionContext: Xrm.Events.EventContext): void {
const formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
if (!formContext) {
console.error('Form context not available');
return;
}
// Your logic here
}
Use Cases
This development workflow is perfect for:
- Complex form logic requiring type safety
- API integrations with external services
- Advanced validation scenarios
- Data manipulation and calculations
- Teams wanting modern development practices
- Long-term maintenance of web resource code
Getting Started
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/Cliveo/Power-Platform-JavaScript-Compiler.git - Install dependencies:
npm install -
Set up Power Platform Git integration and export your solution to the
src/folder - Create your first TypeScript mapping:
npm run new-webresource - Start developing:
npm run dev
Conclusion
The Power Platform JavaScript Compiler transforms web resource development by bringing modern TypeScript tooling to the Power Platform ecosystem. By leveraging Git integration, we can maintain the native Power Platform deployment experience while gaining the benefits of type safety, IntelliSense, and modern development practices.
The project is open-source and available on GitHub. I encourage you to try it out, contribute improvements, and share your experiences with the community.
Happy coding with TypeScript and Power Platform! 🎉
Have questions about the TypeScript workflow or want to share your own Power Platform development tips? Feel free to reach out or contribute to the project on GitHub!